2025 How to Optimize Vanadium Redox Flow Battery Efficiency and Performance
As the demand for renewable energy storage solutions continues to grow, the optimization of the Vanadium Redox Flow Battery (VRFB) has become a focal point in energy technology discussions. According to a recent market analysis by ResearchAndMarkets.com, the global VRFB market is projected to reach $1.14 billion by 2025, driven by its unique advantages of scalability and longevity. This technology stands out in energy storage applications, particularly for utility-scale projects, owing to its ability to store energy for extended periods and discharge it over prolonged durations.
Dr. Emily Chen, a leading expert in the field of battery technology, highlights the importance of optimizing VRFB performance by stating, “Enhancing the efficiency of Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries not only boosts their economic viability but also solidifies their role in the transition to sustainable energy systems.” As we explore the top five strategies to optimize the efficiency and performance of VRFBs in 2025, it is essential to address the current challenges and opportunities that this technology faces. By focusing on advancements in battery chemistry, system integration, and control algorithms, the potential of VRFBs can be fully realized, paving the way for a more resilient and sustainable energy future.
Strategies for Enhancing Ion Exchange Efficiency in Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries
Vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFBs) hold promise for large-scale energy storage due to their long cycle life and inherent safety. However, to fully harness their potential, optimizing ion exchange efficiency is crucial. This can be achieved by improving the design of membranes used in the flow cells. The selection of highly conductive and selective membranes can significantly enhance the movement of vanadium ions, thereby boosting overall performance.
**Tips:** Consider utilizing ion-selective membranes specifically tailored for vanadium ions. Research has shown that materials with lower resistance can lead to increased power output. Additionally, regular maintenance of the flow battery system, including regular checks on the state of the membrane, can prevent degradation and maintain efficiency.
Another strategy involves optimizing the electrolyte concentration. Increasing the concentration of vanadium ions can enhance the kinetic response, allowing for faster ion transfer rates. However, it's essential to strike a balance to avoid issues such as precipitation.
**Tips:** Conduct experiments to find the optimal electrolyte concentration while monitoring for any adverse effects. Utilizing additives that stabilize the electrolyte can also contribute to improved ion exchange efficiency and enhance overall battery life.
Innovative Membrane Technologies to Improve Voltage Efficiency in Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries
Innovative membrane technologies are at the forefront of enhancing the voltage efficiency of vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFBs), a sector poised for substantial growth with a projected CAGR of 19.9%. The implementation of advanced membrane materials, such as pyridine-containing membranes, has shown a significant increase in conductivity and overall performance, addressing the challenges of energy loss during operation.
Membrane-free configurations are also emerging, allowing for higher voltages and energy densities, which can further optimize the applications of VRFBs in large-scale energy storage solutions.
Tips for optimizing the efficiency of VRFBs include focusing on asymmetric electrolyte flow rates, which studies have demonstrated can enhance overall battery performance. Additionally, exploring robust membrane materials that minimize ion transport resistance will provide a competitive edge in the market. Engaging with startups innovating in the energy storage sector can also offer fresh insights and potential collaborations that drive further advancements in battery technology.
With the increasing demand for sustainable energy storage options, the innovations in membrane technology and redox flow battery designs will play vital roles in meeting global energy needs. As the market expands, staying informed about these trends and investing in state-of-the-art solutions will be essential for businesses aiming to thrive in this evolving landscape.
Impact of Temperature Regulation on Vanadium Redox Flow Battery Performance Metrics
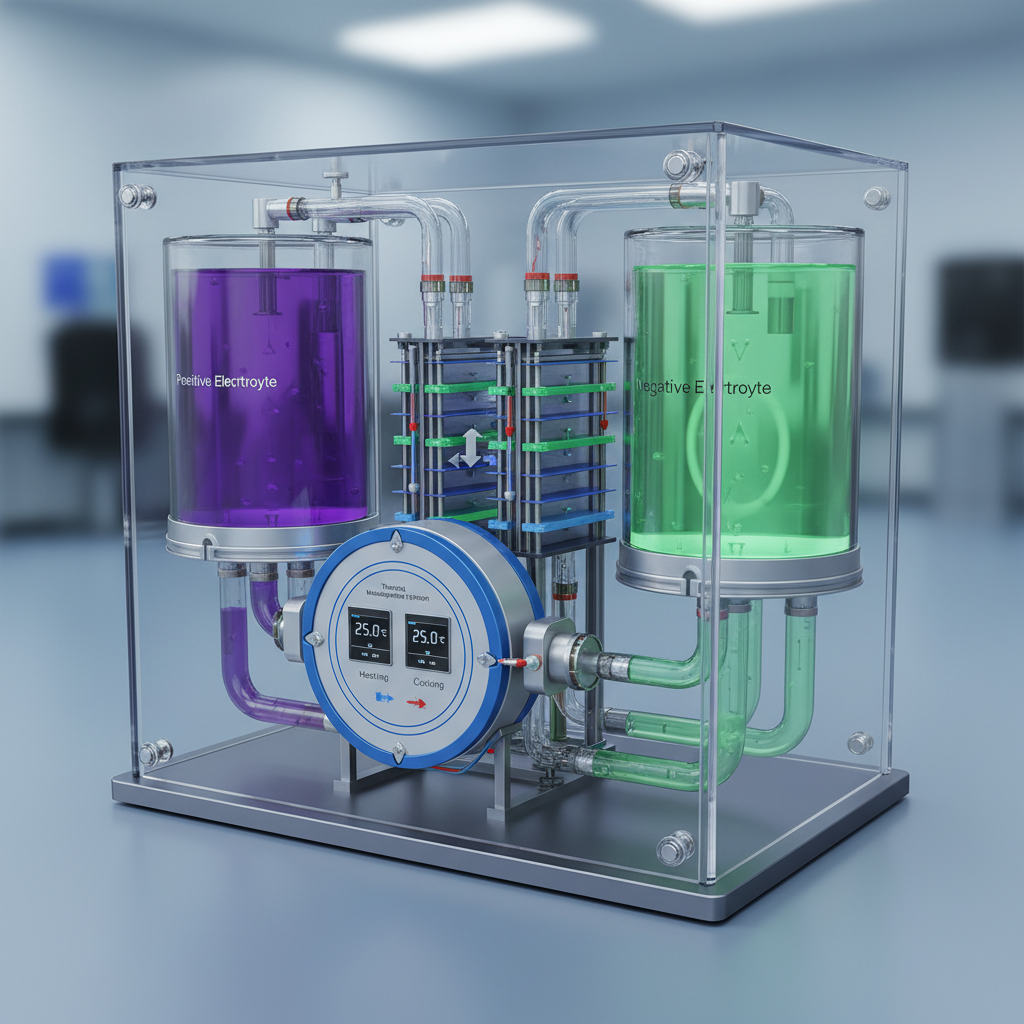

Temperature regulation plays a crucial role in optimizing the performance metrics of vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFBs). As the temperature fluctuates, the viscosity of the electrolytes varies, affecting the ionic conductivity and overall charge transfer efficiency within the system. Higher temperatures can enhance reaction kinetics, leading to improved discharge rates. However, excessive heat can also cause degradation of the electrolyte and other materials, resulting in reduced battery lifespan. Thus, maintaining an optimal temperature range is vital for maximizing efficiency.
Additionally, temperature regulation influences the overall energy density and round-trip efficiency of VRFBs. A controlled thermal environment allows for stable performance during charge and discharge cycles, ensuring that energy loss through thermal management is minimized. By employing advanced materials and design strategies to enhance thermal conductivity and insulation, the performance of VRFBs can significantly improve. Innovative cooling systems can also be integrated to dissipate heat effectively, thereby maintaining optimal conditions that facilitate better ion flow and reaction rates, ultimately leading to superior operational efficiency.
Analyzing the Role of Electrolyte Concentration on Energy Density in Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries
The efficiency and performance of Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries (VRFBs) are critically influenced by the concentration of the electrolyte used. A higher electrolyte concentration can lead to increased energy density, which is vital for large-scale energy storage applications. Recent studies have shown that optimizing electrolyte concentration not only enhances energy efficiency but also improves the battery's overall stability under various operational conditions, including low temperatures. Researchers are actively investigating these relationships to develop advanced battery systems that can better integrate with renewable energy sources.
**Tips:** When working with VRFBs, always consider the compatibility of your electrolyte with the other components of the battery system. Experimenting with various concentrations can lead to significant performance improvements. Additionally, pay attention to the effects of temperature on electrolyte stability; this could prevent potential degradation of battery performance.
The ongoing advancements in VRFB technology, such as the exploration of asymmetrical flow rate designs and novel electrolyte compositions, hold promise for further enhancing battery capabilities. As the demand for reliable energy storage solutions grows, focusing on these key parameters will be essential for unlocking the full potential of Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries in supporting a sustainable energy grid.
Evaluating Long-Term Cycling Stability of Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries for 2025 Applications
The performance and long-term cycling stability of vanadium redox flow batteries (VRFBs) are crucial as the demand for efficient energy storage systems increases. Evaluating the durability of these batteries involves assessing various factors, including electrolyte formulations and charge-discharge cycles. Recent advancements highlight the significance of optimizing factors such as temperature and flow rates to enhance performance while ensuring longevity.
Tips for maximizing the cycling stability of VRFBs include regular monitoring of electrolyte concentrations and maintaining appropriate operating temperatures. It's essential to conduct routine assessments of the battery components, including the membrane and electrodes, as these can significantly impact overall performance. Additionally, utilizing advanced materials, such as polymer electrolytes or new electrode designs, can lead to improvements in efficiency and lifecycle.
Investing in research focused on innovative battery designs, such as membrane-free configurations, could also pave the way for breakthroughs in VRFB technology. Collaborating with industry experts and researchers will be vital to continue pushing the boundaries of energy storage capabilities and finding solutions to common challenges faced by vanadium redox flow batteries.
2025 Vanadium Redox Flow Battery Efficiency and Performance
This chart illustrates the capacity retention of Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries over a series of cycling tests. As shown, a steady decline in capacity occurs over time, highlighting the importance of optimizing battery efficiency and long-term cycling stability for future applications.
Related Posts
-

Energy Storage Battery Innovations Projected Growth Trends at 2025 China Import and Export Fair
-

Exploring the Future of Energy Storage with the Best Lithium Polymer Battery Technology
-

Understanding the Future of Energy Storage Battery Technology Innovations and Applications
-

The Complete Guide to Choosing the Best Flow Batteries for Your Energy Needs
-

Unleashing Chinese Innovation in Mobile Battery Technology for Global Market Success
-
How to Ensure Import Export Certification for the Best Vacuum Circuit Breaker
