What is Power Energy Battery and How Does It Work?
The Power Energy Battery has become a critical component in modern energy solutions. Experts in the field emphasize its importance. Dr. Emily Chen, a renowned energy analyst, famously stated, “Power Energy Batteries are revolutionizing how we store and utilize energy.” This sentiment reflects a growing understanding of these batteries in our renewable energy landscape.
Understanding how a Power Energy Battery works requires an exploration of its components and technology. These batteries store electrical energy, providing reliable power sources for various applications. From homes to electric vehicles, their impact is profound. However, there are ongoing debates about their efficiency and environmental impact. Critics highlight issues related to the production and recycling of battery materials.
Despite these challenges, the potential of Power Energy Batteries is undeniable. As technology evolves, improvements in design and function continue to emerge. The journey of this technology is just beginning, and its future holds promise. Striking a balance between advancement and sustainability remains a key discussion point. The conversation around Power Energy Batteries is not just about innovation; it’s about responsibility.

What is a Power Energy Battery?
Power energy batteries are essential components in the modern energy landscape. They store energy for various applications, from electric vehicles to renewable energy systems. These batteries operate by converting chemical energy into electrical energy. When charged, a chemical reaction occurs, which allows energy to be stored. Upon discharge, this stored energy is released.
According to a report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), global battery demand is set to surge. It is expected to increase by 30% annually through 2030. Lithium-ion batteries dominate the market due to their efficiency and energy density. However, other battery types, such as solid-state and flow batteries, are emerging. They promise even better performance and safety.
Despite their advantages, power energy batteries face challenges. Recycling methods are not yet fully developed. Environmental concerns about lithium mining are also significant. As the industry grows, addressing these issues is crucial. Without improvement, we risk repeating past mistakes in energy consumption. This evolution in battery technology reveals both potential and pitfalls.
Key Components and Structure of Power Energy Batteries
Power energy batteries are at the heart of modern energy storage solutions. They consist of several key components that work together to store and release electrical energy efficiently. The main parts include electrodes, electrolytes, and separators. Each element plays a crucial role in optimizing the battery’s performance.
Electrodes are critical. One electrode stores positive ions, while the other stores negative ions. This setup creates a potential difference. The electrolyte facilitates the movement of ions between the electrodes. It must be effective to ensure quick energy discharge and charge. Separators, on the other hand, prevent short circuits by keeping the electrodes apart. They are vital for safety and longevity.
Tip: When selecting a power energy battery, consider the specific applications. Not all batteries serve the same purpose. Some may perform poorly under heavy loads.
The structure of these batteries might seem simple but is quite complex. Manufacturing quality varies, which can affect performance. Some batteries may not deliver as promised. It’s essential to reflect on these limitations. Understand that there may be better options available.
Tip: Regular maintenance can enhance the lifespan of power energy batteries. Keeping them clean and at optimal temperatures helps prevent performance degradation.
How Power Energy Batteries Store and Release Energy
Power energy batteries are essential for modern technology. They store energy from renewable sources like solar and wind. The process is fascinating, albeit complex.
When energy is stored, it typically happens through electrochemical reactions. These reactions occur within the battery cells. Electrons are transferred between materials, creating a charge. As a result, energy is accumulated for future use. During discharge, the stored energy is released. This occurs when the electrons flow back, powering devices.
While this technology is promising, it’s not without flaws. Efficiency can vary widely. Some batteries degrade faster than expected. This raises concerns about sustainability. Research is ongoing, and improvements are needed. The challenge lies in maximizing performance while minimizing environmental impacts.
Common Applications of Power Energy Batteries
Power energy batteries play a crucial role in modern technology. They store energy for various applications. Many people rely on them daily without realizing their importance.
In electric vehicles, power energy batteries are essential. They provide the energy needed for long distances. Charging stations are popping up everywhere, making electric vehicles more accessible. However, range anxiety remains a concern for many drivers. Some worry if they can find a charging point in time.
Power energy batteries are also key in renewable energy systems. They store excess solar or wind energy for later use. This helps reduce dependency on traditional energy sources. Yet, efficiency loss during energy conversion is still an issue. Some systems waste potential power, which is frustrating.
As technology evolves, addressing these challenges is vital for a sustainable future.
Future Trends in Power Energy Battery Technology

The power energy battery market is evolving rapidly. According to a recent report by BloombergNEF, the global battery market is projected to grow to $620 billion by 2030. In this scenario, advancements in energy density are crucial. Enhancements of battery capacity are vital for electric vehicles and renewable energy storage. However, challenges remain, particularly regarding materials and recycling.
Another interesting trend is the shift towards solid-state batteries. This technology promises higher energy density and improved safety. A McKinsey study indicates that solid-state batteries could reduce the cost per kilowatt-hour significantly by 2030. Yet, scalability remains an issue. Current production methods are costly and complex. Companies must address these obstacles to reap the benefits fully.
The emphasis on sustainability is also notable. A circular economy model for batteries is gaining traction. Research shows that recycling could recover up to 95% of materials like lithium and cobalt. Still, the approach is not widespread enough. Greater investment in recycling technology is needed. The trajectory of power energy batteries is promising, yet many questions linger.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Power Energy Battery Solutions for Efficient Use?
-
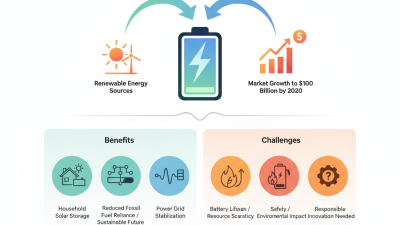
Why Are Power Energy Batteries Essential for the Future?
-
Unlocking the Future: Advantages of the Best Energy Storage LiFePO4 Battery for Global Buyers
-

Unlocking the Power of Best Power Storage Battery Specifications and How to Choose the Right One for Your Needs
-

5 Best Strategies for Power Storage Battery Efficiency
-

Essential Power Storage Battery Maintenance Checklist for Optimal Performance
