Top 10 Power Energy Batteries for Your Needs in 2026?
The demand for Power Energy Batteries is rapidly growing. By 2026, the market is expected to exceed $200 billion. This growth is driven by increasing energy needs and advancements in technology. According to a recent report from BloombergNEF, the global demand for energy storage solutions will triple by 2030.
Leading industry expert Dr. Emily Chen states, "The future of Power Energy Batteries is not just about capacity. It's about efficiency and sustainability." Her insights reflect the current shift towards eco-friendly energy solutions. As we explore the top ten Power Energy Batteries for your needs, we must consider their environmental impact alongside their performance.
Amidst the exciting advancements, challenges remain. Many batteries still face issues with recycling and resource sourcing. This brings a layer of complexity to the innovation landscape. The future could be bright for Power Energy Batteries, yet it requires ongoing reflection and improvement.

Top Power Energy Battery Technologies Revolutionizing 2026 Market
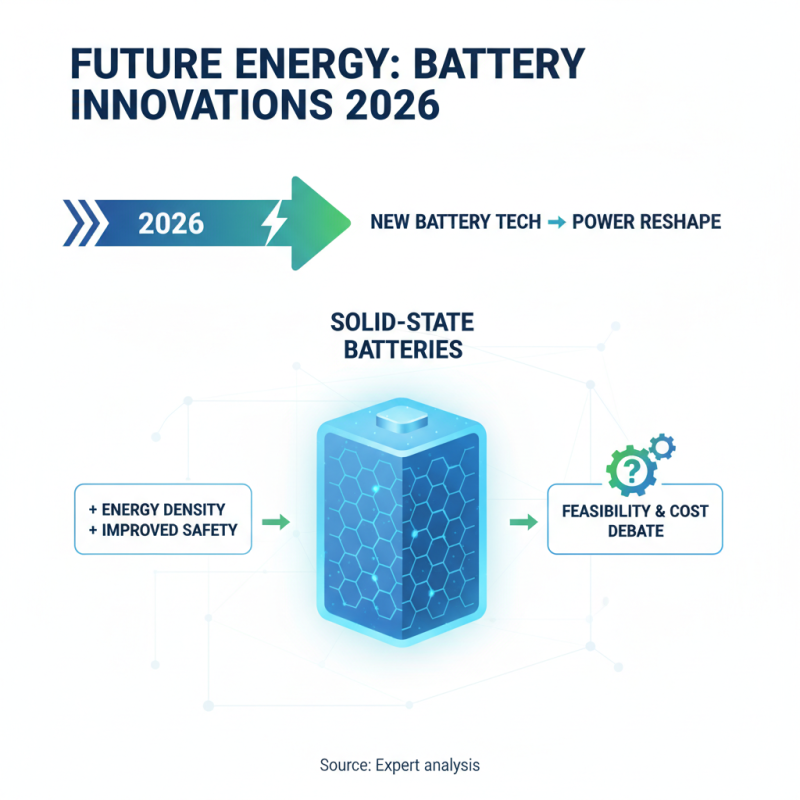
The energy landscape is changing rapidly. In 2026, new battery technologies will reshape power consumption. Solid-state batteries may dominate this market. They promise increased energy density and improved safety compared to current lithium-ion batteries. Some experts argue about feasibility and costs, though.
Another game-changer could be lithium-sulfur batteries. They offer higher capacities and longer lifespans. However, efficiency remains a challenge. Imagine a battery that lasts for weeks on a single charge. It's a goal, but not yet reality.
Finally, flow batteries are gaining attention. They are ideal for large-scale storage solutions. Yet, their bulkiness poses limitations. The search for smaller, efficient designs continues. Each innovation brings hope, but also uncertainty.
Key Features to Consider When Choosing Power Energy Batteries
When choosing power energy batteries, several key features should be on your radar.
Energy density is crucial. A higher energy density means batteries can store more energy in a smaller space.
According to recent industry reports, the demand for compact batteries is rising. They can be essential for electric vehicles and portable devices.
However, focusing solely on density can lead to compromises in safety.
Another important aspect is charge cycle durability. The more cycles a battery can endure, the longer its lifespan.
Recent studies suggest that batteries with over 3000 charge cycles perform better in long-term applications.
Users should be wary of lower cycle counts. These can lead to increased costs over time. Additionally, assess thermal stability. This can impact the battery's performance in extreme conditions.
Lastly, consider environmental impact. Many consumers now prioritize sustainability.
Some batteries have recyclability rates as low as 30%. This not only affects the environment but also future regulations.
It's vital to explore technology advancements in this area. Choices today will shape the market in 2026 and beyond.
Comparative Analysis of the Leading Power Batteries for 2026
When considering power energy batteries for 2026, several key factors emerge. The landscape is shifting rapidly. Energy density, charge time, and longevity stand out as crucial metrics. You need a battery that meets demands. Higher energy density translates to longer use without frequent recharges. This is essential for electric vehicles and renewable energy systems.
The charge time also plays a critical role. A battery that charges quickly can significantly enhance user experience. While some newer options promise rapid charging, they might compromise on longevity. Balance is key. It’s not just about quick fixes; durability matters too.
Tips: Focus on the application. Different settings may require different battery types. Analyze your specific needs carefully. Watch out for warranties; they can offer insights into a battery's reliability. Remember, new technology often comes with growing pains. It’s wise to research reviews and user experiences before purchasing.
Top 10 Power Energy Batteries for Your Needs in 2026
Sustainability and Environmental Impact of Future Battery Technologies

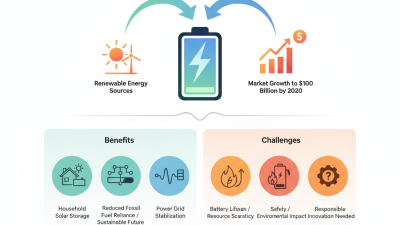
As we look towards 2026, the demand for sustainable power energy solutions grows. Future battery technologies must prioritize environmental impact. Researchers are focusing on materials that reduce carbon footprints. For example, using abundant and renewable resources can minimize dependence on rare minerals. This shift is essential in ensuring a sustainable supply chain.
Tips: Always consider battery recycling options. Many new technologies incorporate recyclable materials to aid sustainability. It's crucial to explore products that promote a circular economy.
Another aspect is energy efficiency. Innovations aim to create batteries that last longer and charge faster. However, the production processes must also be cleaner. Manufacturing should use renewable energy sources to reduce emissions. We still face challenges in achieving this goal. Key players in the industry must invest in cleaner methods.
Tips: Look for batteries with high energy density. These batteries require less material for the same output. This low-impact approach may help the environment significantly.
Predicted Trends and Innovations in Power Energy Storage Solutions
In 2026, energy storage solutions will evolve dramatically. Industry reports suggest that demand for power energy batteries will surge by 40%. As renewable energy sources like solar and wind grow, efficient battery systems become crucial. Innovations in lithium-sulfur and solid-state batteries may redefine efficiency and longevity. These technologies promise higher energy density. They can potentially offer 50% more capacity than current lithium-ion solutions.
However, challenges remain. Production costs for advanced battery materials are still high. Recycling processes for old batteries need improvement. According to the International Energy Agency, only 10% of used batteries are recycled effectively today. This indicates a significant area for growth. There is a pressing need to develop sustainable practices. Additionally, regulatory frameworks must adapt to support emerging technologies.
As we look ahead, user needs will shape the market. From electric vehicles to grid storage, versatility is key. Customers want batteries that are long-lasting and cost-effective. The next few years will be pivotal. Companies must innovate while addressing environmental impacts. Sustainability will not be optional. The focus must shift toward creating batteries that benefit both users and the planet.
Top 10 Power Energy Batteries for Your Needs in 2026
| Battery Type | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Cycle Life (Cycles) | Charge Time (Hours) | Cost ($/kWh) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium-ion | 250 | 2000 | 1 | 150 |
| Solid State | 400 | 5000 | 2 | 200 |
| Lithium Sulfur | 350 | 600 | 1.5 | 180 |
| Flow Battery | 40 | 10000 | 4 | 300 |
| Nickel-Metal Hydride | 100 | 1000 | 1 | 250 |
| Lithium Titanate | 200 | 20000 | 0.5 | 400 |
| Zinc-ion | 120 | 2500 | 2 | 130 |
| Lead-acid | 30 | 500 | 8 | 150 |
| Sodium-ion | 120 | 3000 | 1.5 | 100 |
| Aluminum-air | 810 | 30 | 3 | 250 |
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Power Energy Battery Solutions for Efficient Use?
-

What is Power Energy Battery and How Does It Work?
-

Unlocking the Power of Best Power Storage Battery Specifications and How to Choose the Right One for Your Needs
-
Unlocking the Future: Advantages of the Best Energy Storage LiFePO4 Battery for Global Buyers
-

5 Top Battery Storage Solutions Revolutionizing Energy Management in 2023
-
Why Are Power Energy Batteries Essential for the Future?
