Why Do Lithium Car Batteries Last So Long?
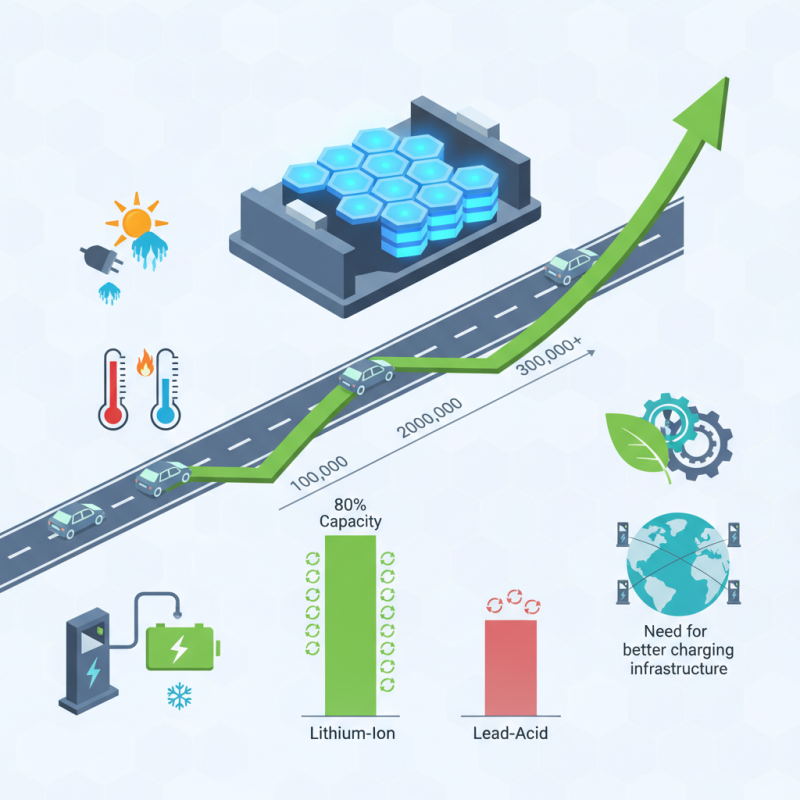
Lithium car batteries are revolutionizing the automotive industry. With impressive longevity, these batteries power electric vehicles (EVs) for thousands of miles. Reports show that lithium battery technology can achieve over 300,000 miles of usable life. This durability is a game-changer for consumers and manufacturers alike.
Experts note that lithium car batteries have a life cycle that exceeds traditional lead-acid batteries by a significant margin. Data indicates that lithium batteries can maintain up to 80% of their capacity even after many cycles. In contrast, lead-acid batteries often fail after just a few hundred cycles. However, there are challenges to consider. Factors like temperature extremes and charging habits can affect battery life.
The efficiency of lithium car batteries highlights the need for better charging infrastructure. As these batteries become more popular, ensuring reliable charging stations is crucial. The industry must reflect on improving battery technology while considering sustainability. Lithium car batteries mark progress, yet the journey is far from perfect.
Understanding the Chemistry of Lithium-Ion Batteries in Electric Vehicles
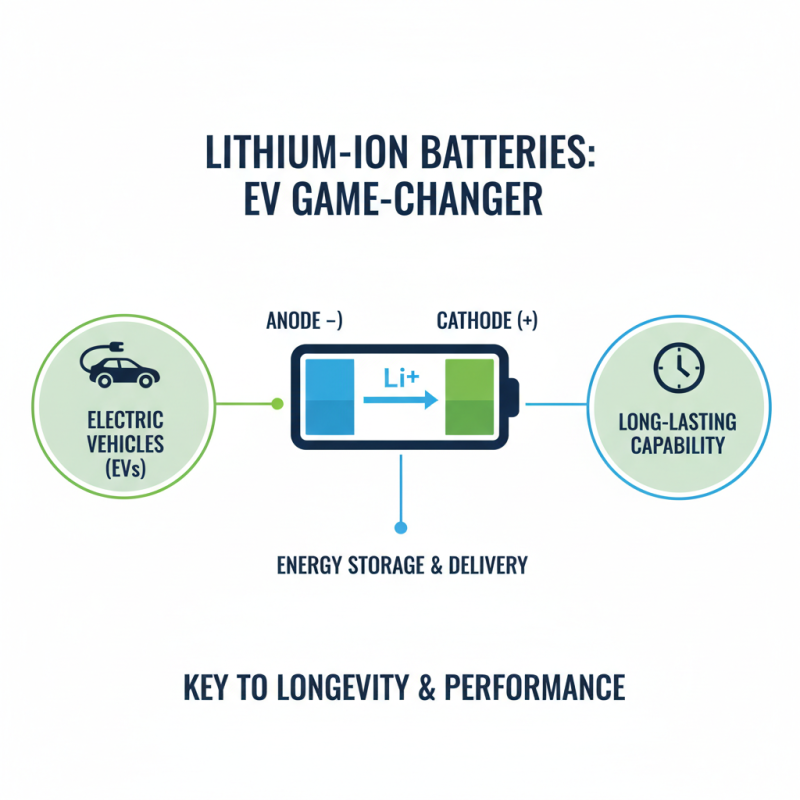
Lithium-ion batteries are a game changer for electric vehicles (EVs). Their ability to last long is rooted in their chemical structure. These batteries rely on lithium ions moving between two electrodes. This movement facilitates energy storage and delivery, which is key to longevity.
Research indicates that lithium-ion batteries can maintain up to 80% of their capacity even after 2,000 charge cycles. They have a high energy density, typically around 150-200 Wh/kg. This means they can store more energy in a smaller size, unlike lead-acid batteries, which are bulkier and less efficient. It’s clear that lithium batteries come with advantages, but there are drawbacks too.
Despite their efficiency, lithium batteries face thermal management issues. They can overheat if not properly cooled. Additionally, their performance may degrade in extreme temperatures. A report by the International Energy Agency highlights that 10% of lithium-ion battery energy is lost through heat. This raises concerns about efficiency and durability. As manufacturers navigate these challenges, the chemistry behind lithium-ion batteries continues to evolve, promising even more effective solutions.
The Role of Battery Management Systems in Enhancing Lifespan
Battery Management Systems (BMS) play a crucial role in extending the lifespan of lithium car batteries. They monitor each cell's voltage and temperature. Keeping these metrics within safe limits prevents overheating and overcharging. Over time, these factors can degrade battery health. A BMS can detect imbalances among cells, ensuring uniform charging. This helps to maintain capacity over the battery's life.
Moreover, BMS can optimize charging cycles. Lithium batteries perform best when charged to about 80% capacity. A well-designed system can adjust the charging process, reducing stress on the battery. This results in less wear and tear. However, not all systems are perfect. Some may fail to react quickly enough to sudden changes. Such shortcomings can lead to battery inefficiencies. Users might find their batteries aging faster than expected.
In addition, BMS contribute to safety. They shut down the battery in case of anomalies, like short circuits. But, there is always room for improvement. New technologies are emerging to enhance BMS capabilities. The journey toward perfect battery management is ongoing, as engineers seek to push the limits of lithium battery technology. Each innovation can lead to longer-lasting, safer, and more efficient energy storage solutions.
Impact of Temperature and Environmental Factors on Battery Longevity
Temperature and environmental factors play crucial roles in the longevity of lithium car batteries. Extreme heat can accelerate battery degradation. In high temperatures, the chemical reactions inside the battery become more vigorous. This can lead to faster wear and shorter lifespan. Cold weather also poses challenges. Low temperatures can reduce the battery's efficiency, leading to diminished range and performance.
Tips to extend your battery life include keeping your car in a garage or shaded area. This helps regulate temperature and prevents exposure to extreme conditions. Regularly checking the battery health is also essential. Sometimes, minor issues can be addressed before they lead to significant problems.
It's important to note that environmental factors aren't always within our control. Pollution and high humidity can negatively impact battery performance. Reflect on your driving habits as well. Frequent short trips can stress the battery, while longer drives typically promote better health. Consider adjusting your driving patterns to optimize battery life.
Impact of Temperature on Lithium Car Battery Longevity
This chart demonstrates the impact of various environmental temperatures on the lifespan of lithium car batteries. As temperature increases from 0°C to 20°C, battery lifespan reaches its peak at around 10 years. However, extremes above or below this range result in decreased longevity due to factors like chemical reactions and thermal stress.
Comparative Analysis: Lithium-Ion vs. Other Battery Technologies Durability
Lithium-ion batteries are known for their impressive durability compared to other battery technologies. A recent study highlights that lithium-ion batteries can last up to 10 years or more, depending on usage and care. For instance, they maintain about 70-80% of their original capacity even after thousands of charge cycles. In contrast, lead-acid batteries typically last only about 3-5 years and demonstrate a rapid decline in performance.
A significant reason for lithium batteries’ longevity lies in their chemical makeup. They feature a higher energy density, enabling more energy storage in a smaller space. According to the Department of Energy, lithium-ion batteries can achieve more than 1000 charge cycles without significant capacity loss. This is particularly advantageous for electric vehicles, where long-range and reliability are crucial.
Tip: To extend the lifespan of your lithium batteries, avoid deep discharges. Keeping them charged within 20-80% of capacity prolongs their health. Similarly, avoid exposing them to extreme temperatures, as this can accelerate wear and tear. Balancing usage with proper care is essential. Remember, even the best technology requires attention and mindfulness.
Future Innovations in Lithium Battery Technology for Extended Life
Lithium battery technology continues to evolve, promising longer-lasting solutions for electric vehicles. Recent studies reveal that the lifespan of lithium-ion batteries can exceed 1,000 charging cycles. Innovations such as solid-state batteries could enhance this lifespan significantly. These advances may lead to 30% longer battery life, according to industry reports.
Recent advancements focus on improving energy density. Higher energy density means more power with less weight. As a result, vehicles can travel farther on a single charge. Research shows potential for batteries reaching 500 Wh/kg, doubling current standards. This shift could be crucial, especially as more consumers adopt electric vehicles.
Tips: Regularly monitor your battery’s temperature. Keep it within recommended ranges to extend its life. Also, avoid charging to 100% frequently. This can reduce stress on the battery cells.
Another area to watch is recycling technology. As the lithium-ion market expands, sustainability becomes vital. Current practices allow for recovery of nearly 95% of materials in used batteries. This is crucial as demand for lithium increases. The transition to better recycling methods may further impact battery longevity in the future.
Related Posts
-

Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Best Rechargeable Lithium Batteries for Your Devices: Expert Insights & Data
-

The Future of Energy Storage Exploring the Benefits of Rechargeable Lithium Batteries in Sustainable Technology
-
2025 Top Lithium Car Battery Innovations for Electric Vehicle Efficiency
-

Mastering the Essentials of Lithium Ion Car Battery Maintenance for Longevity
-

Why Lithium Ion Car Batteries Are Revolutionizing Electric Vehicles Today
-

Top 10 Benefits of Lithium RV Batteries for Your Adventures?
